Being lesser known cannabinoids CBG, CBC, and CBN can be difficult to find in isolated forms, with only a few reputable suppliers manufacturing these isolates. On the other hand, you may have better luck finding products that have higher amounts of these lesser known cannabinoids. Keep in mind that these compounds typically are more effective as a group; this is known as the entourage effect.
CBC (Cannabichromene)
Let’s get into it with CBC…Cannabichromene is a rare, non-psychoactive cannabinoid, usually found at low levels of <1% when present. Some research has suggested that CBC may work as an antibiotic and may be effective in combating bacterial infections. CBC also appears to reduce pain, work as a potent anti-inflammatory agent, act as an antidepressant, and ease the symptoms of menopause.
Surprisingly, CBC has shown the potential to not only protect the brain, but actually encourage it to develop new brain cells in the areas specifically responsible for memory and learning. When the brain discontinues development of new cells in these areas, individuals become at higher risk for neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s. CBC may be a great aid in preventing or delaying the onset of such conditions; this has resulted in some patients using the compound for its potential neuroprotectant properties.
CBN (Cannabinol)
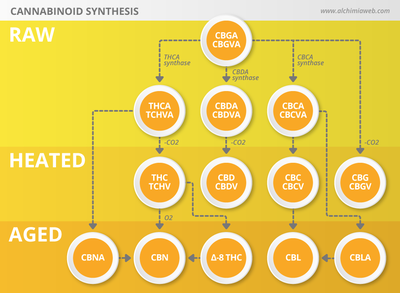
THC ages we get a cannabinoid with a wide range of effects known as CBN. Essentially cannabinol is an oxidative degradation product of THC. It may result from improper storage or curing and extensive processing, such as when making concentrates. It is usually formed when THC is exposed to UV light and oxygen over time. Although some see this conversion as a bad thing, there are others that prefer cannabis that has reached this stage as its effects change.
If you have sleeping troubles then CBN may be the cannabinoid for you as it is potentially the most sedative cannabinoid researched. Many users of Cannabinol use it for these sedative effects to treat or ease insomnia.
CBN has also shown positive effects in appetite stimulation for patients suffering from anorexia, cancer, and other conditions that have a negative impact towards appetite.
Research also suggests that CBN works as a powerful antibiotic. Along with CBC, CBN has been shown to effectively treat antibiotic-resistant infections like methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
Patients suffering from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) or Lou Gehrig’s disease may find some relief with CBN as studies have found it helpful in slowing the disease’s progression. Researchers were able to delay the onset of ALS symptoms in mice treated with CBN, showed one study.
According to additional research, CBN showed to be effective in patients with glaucoma by effectively lowering ocular pressure. Ocular pressure is the symptom which can cause blindness in glaucoma patients.
CBG (Cannabigerol)
Last but certainly not least we have CBG. Cannabigerol is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid commonly found in cannabis. CBGa is the precursor to both THCa and CBDa in the plant usually found at low levels of <1% when present.
Similar to CBC and CBN, CBG has also been shown to have antibiotic properties. That isn’t the only potential use of this cannabinoid however.
CBG has showed promising results as a powerful pain reliever and may even be more effective than THC or CBD. Due to these pain relieving properties, CBG may also be effective with the side effects of menopause. With that being said, CBG has also been shown to help prevents bone loss and the onset of osteoporosis after menopause.
Among the benefits of CBG include patients that use the compound to regulate their emotions. Research has shown that CBG raises serotonin levels in the brain, giving promises that it could work as a moderate antidepressant.
In closing, this cannabinoid also has been shown to have anti-tumor properties, and the potential to be especially helpful for individuals with skin cancer. CBG also has the potential to help with other skin conditions including alleviating psoriasis by preventing reddening of the skin.










